Are you considering purchasing a home but not sure what type of mortgage is right for you? Look no further! In this article, we will explore the different types of mortgages available, including fixed-rate, adjustable-rate, FHA, and VA loans. Each type has its own unique features and benefits, and by understanding these options, you can make an informed decision that best suits your financial needs. Whether you’re a first-time homebuyer or looking to refinance your existing mortgage, this article will provide you with the information you need to confidently navigate the world of mortgages and achieve your homeownership goals. When it comes to securing a mortgage, there are various types available to meet the diverse needs and financial circumstances of borrowers. Understanding the differences between these mortgage options is crucial in making an informed decision that aligns with your homeownership goals. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the different types of mortgages, including their definitions, how they work, advantages, disadvantages, and various factors to consider in choosing the right mortgage for you.
Fixed-rate Mortgages
Definition of Fixed-rate Mortgages
A fixed-rate mortgage is a type of home loan where the interest rate remains the same throughout the entire term of the loan. This means that your monthly payments will also remain consistent, which provides stability and predictability in your budgeting.
How Fixed-rate Mortgages Work
With a fixed-rate mortgage, the interest rate is determined at the beginning of the loan term and remains fixed over the entire duration of the loan, whether it is 15, 20, or 30 years. This means that regardless of the fluctuations in the broader economy or interest rate market, your mortgage interest rate will not change.
Advantages of Fixed-rate Mortgages
One significant advantage of a fixed-rate mortgage is the stability it provides. Knowing that your interest rate and monthly payments will remain the same for the duration of your loan term allows for better budgeting and financial planning. Additionally, fixed-rate mortgages are especially beneficial in a low-interest-rate environment, as borrowers can lock in a favorable rate for the long term.
Disadvantages of Fixed-rate Mortgages
The main disadvantage of a fixed-rate mortgage is that the initial interest rates may be slightly higher compared to adjustable-rate mortgages, especially in a low-interest-rate environment. Additionally, if interest rates in the market significantly drop after you secure your fixed-rate mortgage, you would not be able to take advantage of the lower rates without refinancing your mortgage, which incurs additional costs.
Adjustable-rate Mortgages
Definition of Adjustable-rate Mortgages
An adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM), also known as a variable-rate mortgage, is a home loan where the interest rate can fluctuate over time. The initial interest rate is typically lower than that of a fixed-rate mortgage, but it can adjust periodically according to market conditions.
How Adjustable-rate Mortgages Work
With an adjustable-rate mortgage, the interest rate is fixed for an initial period, usually ranging from 3 to 10 years. After the initial fixed-rate period, the interest rate adjusts periodically based on a predetermined index (such as the U.S. Treasury rate) and a margin set by the lender. The adjustment frequency, such as annually or every few years, may vary depending on the loan terms.
Advantages of Adjustable-rate Mortgages
One advantage of an adjustable-rate mortgage is the potentially lower initial interest rate compared to fixed-rate mortgages. This can result in lower monthly payments during the initial fixed-rate period. Additionally, if interest rates decrease in the future, borrowers with adjustable-rate mortgages may benefit from lower rates without the need to refinance.
Disadvantages of Adjustable-rate Mortgages
The main disadvantage of an adjustable-rate mortgage is the uncertainty it presents. As the interest rates can fluctuate, borrowers may experience higher monthly payments if the rates rise in the future. This lack of stability can make budgeting and financial planning challenging. However, many ARM loans have caps and limits on how much the interest rate can adjust to mitigate potential large increases.
This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
FHA Mortgages
Definition of FHA Mortgages
FHA mortgages are home loans insured by the Federal Housing Administration (FHA). These loans are designed to make homeownership more accessible for individuals who may have difficulty qualifying for conventional mortgages due to lower credit scores, limited down payment funds, or other factors.
How FHA Mortgages Work
FHA mortgages are offered by FHA-approved lenders and provide borrowers with more flexible eligibility requirements and lower down payment options. The FHA insures the loan, which reduces the risk for lenders and allows them to offer more favorable terms to borrowers. However, borrowers are required to pay an upfront mortgage insurance premium and an annual mortgage insurance premium for the life of the loan.
Advantages of FHA Mortgages
One major advantage of FHA mortgages is the lower down payment requirement, which is typically as low as 3.5% of the purchase price. This makes homeownership more accessible for individuals who may not have a large amount of savings for a down payment. FHA mortgages also have more lenient credit score requirements compared to conventional loans, making them a viable option for borrowers with lower credit scores.
Disadvantages of FHA Mortgages
One disadvantage of FHA mortgages is the requirement to pay mortgage insurance premiums. The upfront mortgage insurance premium can be financed into the loan, but it will increase the total loan amount. Additionally, borrowers must pay an annual mortgage insurance premium, which adds to the overall cost of the mortgage. FHA mortgages also have loan limits, which may restrict the amount you can borrow depending on your location.
VA Mortgages
Definition of VA Mortgages
VA mortgages are home loans guaranteed by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) and are available to eligible veterans, active-duty servicemembers, and certain surviving spouses. These loans offer favorable terms and benefits to those who have served or are serving in the military.
How VA Mortgages Work
VA mortgages are provided by private lenders and guaranteed by the VA. They offer benefits such as no down payment requirements, no private mortgage insurance (PMI), and potentially lower interest rates. The VA guarantees a portion of the loan, which reduces the lender’s risk and allows them to offer more favorable terms to eligible borrowers.
Advantages of VA Mortgages
The main advantage of a VA mortgage is the ability to purchase a home with no down payment, making homeownership more attainable for eligible veterans and active-duty servicemembers. VA mortgages also do not require private mortgage insurance (PMI), which can result in significant cost savings. Additionally, VA mortgages often have competitive interest rates, making them an attractive option for eligible borrowers.
Disadvantages of VA Mortgages
One potential disadvantage of VA mortgages is the funding fee that borrowers are required to pay. The funding fee is a one-time payment that helps offset the costs of the VA loan program. The amount of the funding fee varies depending on factors such as the borrower’s military category, down payment amount, and whether it is a first-time or subsequent use of a VA loan. However, this funding fee can be rolled into the loan, providing borrowers with the option to finance it.
This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Interest Rates
Definition of Interest Rates
Interest rates refer to the cost of borrowing money and are expressed as a percentage. They play a crucial role in determining the overall cost of a mortgage and the amount of monthly payments.
Impact of Interest Rates on Different Types of Mortgages
Interest rates can have different impacts on different types of mortgages. In fixed-rate mortgages, the interest rate remains constant over the loan term, so changes in interest rates do not affect the monthly payments. However, borrowers with fixed-rate mortgages may choose to refinance if interest rates drop significantly to take advantage of the lower rates.
On the other hand, adjustable-rate mortgages are directly impacted by changes in interest rates. When the interest rates increase, borrowers with adjustable-rate mortgages may experience higher monthly payments. Conversely, if rates decrease, borrowers may see a reduction in their monthly payments.
Factors Affecting Interest Rates
Several factors influence interest rates, including economic conditions, inflation, government policies, and market forces. When the economy is strong and inflation is low, interest rates tend to be lower. Conversely, in times of economic uncertainty or high inflation, interest rates may rise. Additionally, the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions can also influence interest rates in the broader economy.
How to Find the Best Interest Rate for Your Mortgage
To find the best interest rate for your mortgage, it is essential to shop around and compare offers from different lenders. Consider obtaining quotes from various lenders, including banks, credit unions, and online lenders. Be sure to evaluate not only the interest rate but also the associated fees and loan terms. Comparing multiple offers will help you identify the most competitive interest rate and overall favorable terms for your mortgage.
Loan Terms
Definition of Loan Terms
Loan terms refer to the length or duration of the loan, which indicates the period within which borrowers must repay the borrowed amount along with the interest.
Different Loan Terms Available
Mortgage loan terms typically range from 15 to 30 years, although other options may be available. Shorter loan terms, such as 15 or 20 years, offer the advantage of paying off the mortgage more quickly, resulting in substantial interest savings over the life of the loan. Conversely, longer loan terms, such as 30 years, often have lower monthly payments but result in higher overall interest costs.
Choosing the Right Loan Term for Your Needs
Choosing the right loan term depends on your financial goals and circumstances. If you can afford higher monthly payments and want to save on interest costs, a shorter loan term may be suitable. On the other hand, if you prefer lower monthly payments and are comfortable paying more interest over the long term, a longer loan term may be more appropriate. Consider your financial situation, long-term plans, and budget when deciding the loan term that aligns with your needs.
This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Down Payment Requirements
Definition of Down Payment
A down payment refers to the initial payment made by the borrower when purchasing a home. It is a percentage of the purchase price and represents the borrower’s equity in the property.
Down Payment Requirements for Different Types of Mortgages
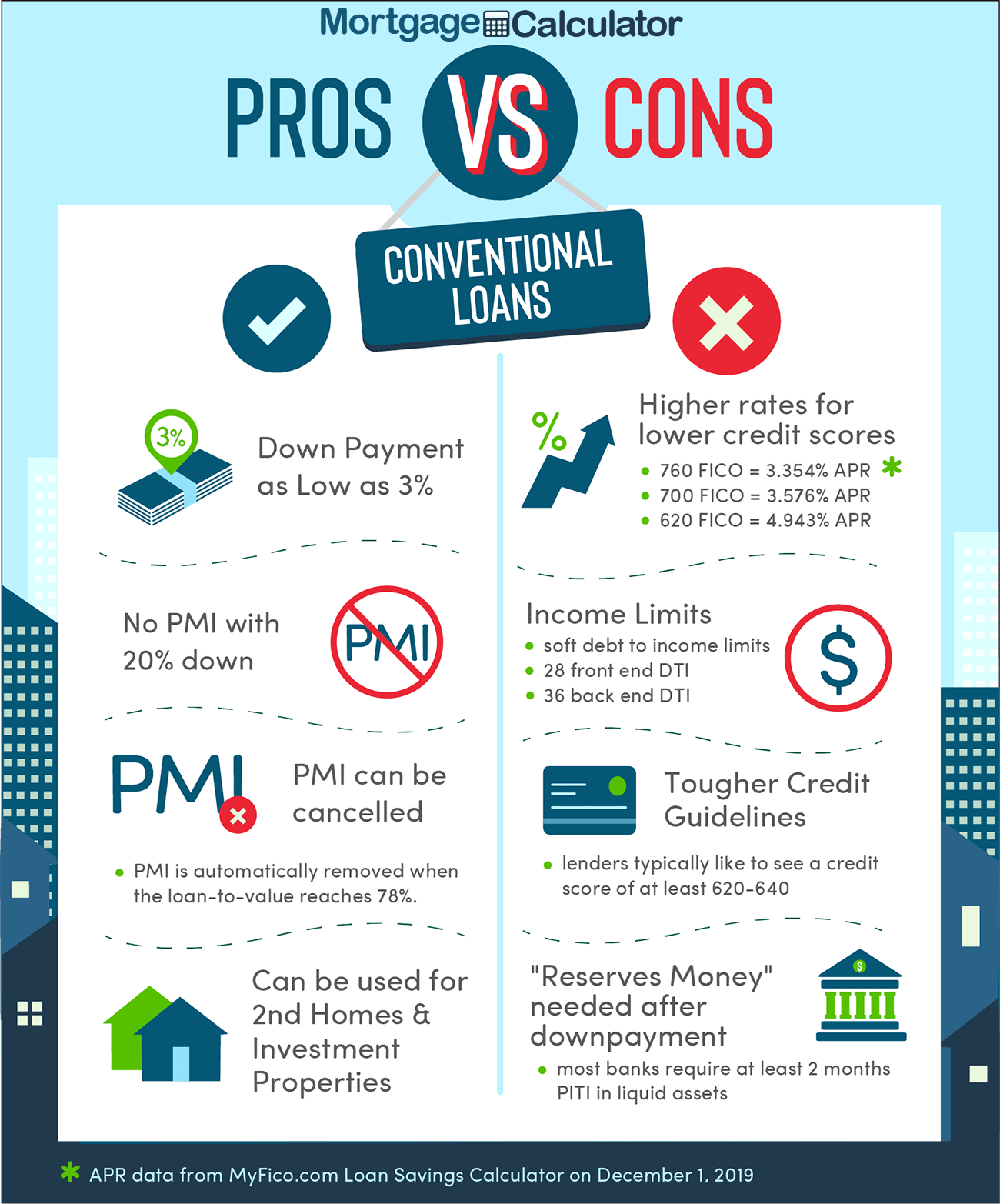
Down payment requirements can vary depending on the type of mortgage. Conventional mortgages typically require a down payment of at least 3% to 20% of the purchase price, depending on the borrower’s creditworthiness. FHA mortgages, as mentioned earlier, allow for a down payment as low as 3.5% of the purchase price. VA mortgages offer the benefit of no down payment requirements for eligible borrowers, making homeownership more accessible for military personnel.
Options for Down Payments
If you are unable to make a large down payment, various options may be available. Down payment assistance programs, offered by state or local housing agencies, can provide financial assistance to eligible borrowers. Additionally, some lenders may offer special programs or loan products with lower down payment requirements. Exploring these options can help you overcome potential barriers to homeownership and secure a mortgage that aligns with your financial situation.
Eligibility Criteria
Definition of Eligibility Criteria
Eligibility criteria refer to the requirements that borrowers must meet to qualify for a specific mortgage program. These criteria may include factors such as credit score, income, employment history, debt-to-income ratio, and property type.
Eligibility Criteria for Different Types of Mortgages
Different types of mortgages have varying eligibility criteria. Conventional mortgages typically require a higher credit score, typically above 620, and a lower debt-to-income ratio. FHA mortgages have more lenient credit score requirements, often accepting scores as low as 500 with a higher down payment. VA mortgages have specific eligibility requirements for veterans, active-duty servicemembers, and surviving spouses, including sufficient military service and honorable discharge.
How to Improve Your Eligibility for a Mortgage
If you do not meet the eligibility criteria for a specific mortgage program, there are steps you can take to improve your eligibility. Some strategies include improving your credit score by making timely payments, reducing outstanding debts, and addressing any errors on your credit report. Increasing your income and reducing your debt-to-income ratio can also enhance your eligibility. Working with a mortgage professional can provide guidance on specific actions to boost your eligibility for the mortgage program you desire.
Closing Costs
Definition of Closing Costs
Closing costs refer to the fees and expenses associated with the purchase or refinancing of a home. These costs are paid at the closing of the mortgage loan and typically include items such as appraisal fees, attorney fees, title insurance premiums, and other miscellaneous charges.
Types of Closing Costs
Closing costs can vary depending on factors such as the loan amount, location, and specific circumstances. Common types of closing costs include appraisal fees, credit report fees, loan origination fees, title search and insurance fees, government recording fees, and prepaid expenses such as property taxes and homeowners insurance.
How to Minimize Closing Costs
While closing costs are an unavoidable part of securing a mortgage, there are ways to minimize these expenses. Comparing loan offers from multiple lenders can help identify lenders with lower closing costs. Additionally, negotiating with the seller to cover some or all of the closing costs can reduce your out-of-pocket expenses. Some lenders may also offer the option to roll the closing costs into the loan amount, although this will increase your overall mortgage balance.
Choosing the Right Mortgage
Factors to Consider
Choosing the right mortgage involves considering several factors to ensure it aligns with your financial goals and circumstances. Some key factors to consider include:
- Interest rates: Evaluate the interest rates offered by different lenders and consider whether a fixed-rate or adjustable-rate mortgage is more suitable for your needs.
- Loan terms: Assess how long you are comfortable making mortgage payments and choose a loan term accordingly.
- Down payment requirements: Determine how much you can afford to put towards a down payment and choose a mortgage program that accommodates your financial situation.
- Eligibility criteria: Review the eligibility criteria for different mortgage programs and determine which ones you are most likely to qualify for based on your credit score, income, and other factors.
- Closing costs: Consider the closing costs associated with each mortgage program and assess whether you have the necessary funds to cover these expenses.
Seeking Professional Advice
Seeking professional advice from a mortgage lender or broker can greatly assist in choosing the right mortgage. These professionals have in-depth knowledge of the mortgage market, can explain the various options available, and provide personalized recommendations based on your financial situation and goals. They can help you navigate the complexities of the mortgage process and ensure you make an informed decision.
Comparing Mortgage Offers
When choosing a mortgage, it is essential to compare offers from multiple lenders to ensure you are getting the best deal. Request loan estimates from various lenders, which will outline the interest rates, loan terms, closing costs, and other relevant details. Review these estimates carefully, paying attention to the interest rate, monthly payment amount, and overall costs over the life of the loan. Comparing multiple offers will enable you to make an educated decision and select the mortgage that best fits your needs and objectives.
In conclusion, understanding the different types of mortgages available is vital in making an informed decision when embarking on the journey of homeownership. Whether you opt for a fixed-rate mortgage, adjustable-rate mortgage, FHA mortgage, or VA mortgage, each comes with its own advantages and disadvantages. Taking into account factors such as interest rates, loan terms, down payment requirements, eligibility criteria, closing costs, and seeking expert advice can help you choose the right mortgage that suits your unique financial circumstances and goals. With the right mortgage in hand, you can turn your dream of homeownership into a reality.